IntroductionA rapid evolution of circuit board production technologies has forced PCB machine manufacturers to develop high performance drilling and routing machines for speed and high precision. In particular, before drilling holes to be used as a reference for the stacking operation of multi-layer boards, the manufacturers have introduced an X-ray inspection operation to determine and compensate the MLB "shrink and stretch" phenomenon. The assembly methodologies for assembling the MLBs may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer but "superimposed", "staggered" or "cornered pads" are now a common practice and this has resulted in an improved drilling precision, which delivers a satisfactory center hole positioning in the drilled PCB stack. Last step in the preparation process is called "STACK PREPARATION" phase. This is the assembly phase that involves putting all the necessary items that generate a pcb stack :
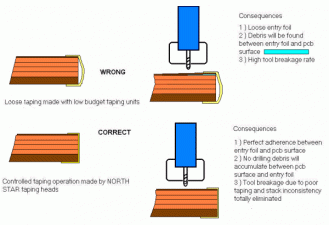
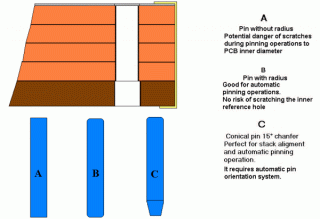
Low technology stacking equipment has shown that poor stacking precision can generate a huge cost at the end of the production process. In particular a loose entry foil can generate a high rate of tool breakage and surface damage to the boards. Misaligned pinning can totally damage the work of the x-ray inspection process and generate a high rate of rejects. Multilink has studied and developed a high precision pinning system, a very sophisticated taping head complete with stack pressure control, a ten Axis Cell controller system denominated FSS for the complete management of any stack production requirement. Multilink complete product line is dedicated to deliver the highest quality results for the pcb stack assembling operation.
Stack assembling operationThe stack assembling machines/systems must be provided with items matching all process specifications:
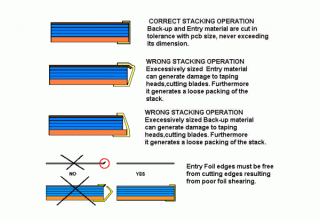
The quality and the performance of the stack assembling system can be heavily reduced if any of the above specifications are not met. The supply of material out of specifications may damage the end result of the stack assembling operation. The following examples of taping and pinning show typical mistakes. The consequences of correct and wrong operations are evidenced. |
|